S.Example 1
Input: {1, 2, 3, 7}, S=6
Output: True
The given set has a subset whose sum is '6': {1, 2, 3}Example 2
Input: {1, 2, 7, 1, 5}, S=10
Output: True
The given set has a subset whose sum is '10': {1, 2, 7}Example 3
Input: {1, 3, 4, 8}, S=6
Output: False
The given set does not have any subset whose sum is equal to '6'.This problem follows the 0/1 Knapsack pattern and is quite similar to Equal Subset Sum Partition. A basic brute-force solution could be to try all subsets of the given numbers to see if any set has a sum equal to S.
So our brute-force algorithm will look like:
for each number 'i'
create a new set which INCLUDES number 'i' if it does not exceed 'S', and recursively
process the remaining numbers
create a new set WITHOUT number 'i', and recursively process the remaining numbers
return true if any of the above two sets has a sum equal to 'S', otherwise return falseSince this problem is quite similar to Equal Subset Sum Partition, let’s jump directly to the bottom-up dynamic programming solution.
We’ll try to find if we can make all possible sums with every subset to populate the array dp[TotalNumbers][S+1].
For every possible sum s (where 0 <= s <= S), we have two options:
Exclude the number. In this case, we will see if we can get the sum s from the subset excluding this number => dp[index-1][s]
Include the number if its value is not more than s. In this case, we will see if we can find a subset to get the remaining sum => dp[index-1][s-num[index]]
If either of the above two scenarios returns true, we can find a subset with a sum equal to s.
Let’s draw this visually, with the example input {1, 2, 3, 7}, and start with our base case of size zero:
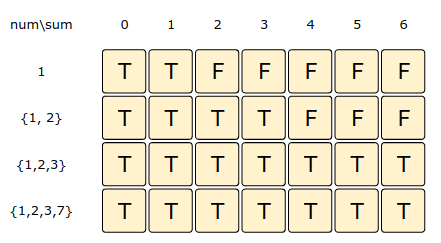
Here is the code for our bottom-up dynamic programming approach:
def can_partition(num, sum):
n = len(num)
dp = [[False for x in range(sum+1)] for y in range(n)]
# populate the sum = 0 columns, as we can always form '0' sum with an empty set
for i in range(0, n):
dp[i][0] = True
# with only one number, we can form a subset only when the required sum is
# equal to its value
for s in range(1, sum+1):
dp[0][s] = True if num[0] == s else False
# process all subsets for all sums
for i in range(1, n):
for s in range(1, sum+1):
# if we can get the sum 's' without the number at index 'i'
if dp[i - 1][s]:
dp[i][s] = dp[i - 1][s]
elif s >= num[i]:
# else include the number and see if we can find a subset to get the remaining sum
dp[i][s] = dp[i - 1][s - num[i]]
# the bottom-right corner will have our answer.
return dp[n - 1][sum]
def main():
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 2, 3, 7], 6)))
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 2, 7, 1, 5], 10)))
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 3, 4, 8], 6)))
main()N represents total numbers and S is the required sum.Can we further improve our bottom-up DP solution? Can you find an algorithm that has space complexity?
def can_partition(num, sum):
n = len(num)
dp = [False for x in range(sum+1)]
# handle sum=0, as we can always have '0' sum with an empty set
dp[0] = True
# with only one number, we can have a subset only when the required sum is equal to its value
for s in range(1, sum+1):
dp[s] = num[0] == s
# process all subsets for all sums
for i in range(1, n):
for s in range(sum, -1, -1):
# if dp[s]==true, this means we can get the sum 's' without num[i], hence we can move on to
# the next number else we can include num[i] and see if we can find a subset to get the
# remaining sum
if not dp[s] and s >= num[i]:
dp[s] = dp[s - num[i]]
return dp[sum]
def main():
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 2, 3, 7], 6)))
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 2, 7, 1, 5], 10)))
print("Can partition: " + str(can_partition([1, 3, 4, 8], 6)))
main()✓→ Minimum Subset Sum Difference