Example 1
Input: "abdbca"
Output: 5
Explanation: LPS is "abdba".Example 2
Input: = "cddpd"
Output: 3
Explanation: LPS is "ddd".Example 3
Input: = "pqr"
Output: 1
Explanation: LPS could be "p", "q" or "r".A basic brute-force solution could be to try all the subsequences of the given sequence. We can start processing from the beginning and the end of the sequence. So at any step, we have two options:
If the element at the beginning and the end are the same, we increment our count by two and make a recursive call for the remaining sequence.
We will skip the element either from the beginning or the end to make two recursive calls for the remaining subsequence.
If option one applies then it will give us the length of LPS; otherwise, the length of LPS will be the maximum number returned by the two recurse calls from the second option.
Here is the code:
def find_LPS_length(st):
return find_LPS_length_recursive(st, 0, len(st) - 1)
def find_LPS_length_recursive(st, startIndex, endIndex):
if startIndex > endIndex:
return 0
# every sequence with one element is a palindrome of length 1
if startIndex == endIndex:
return 1
# case 1: elements at the beginning and the end are the same
if st[startIndex] == st[endIndex]:
return 2 + find_LPS_length_recursive(st, startIndex + 1, endIndex - 1)
# case 2: skip one element either from the beginning or the end
c1 = find_LPS_length_recursive(st, startIndex + 1, endIndex)
c2 = find_LPS_length_recursive(st, startIndex, endIndex - 1)
return max(c1, c2)
def main():
print(find_LPS_length("abdbca"))
print(find_LPS_length("cddpd"))
print(find_LPS_length("pqr"))
main()We can use an array to store the already solved subproblems.
The two changing values to our recursive function are the two indexes, startIndex and endIndex. Therefore, we can store the results of all the subproblems in a two-dimensional array. (Another alternative could be to use a hash-table whose key would be a string (startIndex + “|” + endIndex))
Here is the code for this:
def find_LPS_length(st):
n = len(st)
dp = [[-1 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
return find_LPS_length_recursive(dp, st, 0, n - 1)
def find_LPS_length_recursive(dp, st, startIndex, endIndex):
if startIndex > endIndex:
return 0
# every sequence with one element is a palindrome of length 1
if startIndex == endIndex:
return 1
if (dp[startIndex][endIndex] == -1):
# case 1: elements at the beginning and the end are the same
if st[startIndex] == st[endIndex]:
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = 2 + \
find_LPS_length_recursive(dp, st, startIndex + 1, endIndex - 1)
else:
# case 2: skip one element either from the beginning or the end
c1 = find_LPS_length_recursive(dp, st, startIndex + 1, endIndex)
c2 = find_LPS_length_recursive(dp, st, startIndex, endIndex - 1)
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = max(c1, c2)
return dp[startIndex][endIndex]
def main():
print(find_LPS_length("abdbca"))
print(find_LPS_length("cddpd"))
print(find_LPS_length("pqr"))
main()What is the time and space complexity of the above solution?
dp[st.length()][st.length()] stores the results for all the subproblems, we can conclude that we will not have more than N*NN∗N subproblems (where is the length of the input sequence). This means that our time complexity will be . The above algorithm will be using space for the memoization array. Other than that we will use space for the recursion call-stack. So the total space complexity will be , which is asymptotically equivalent to .
Since we want to try all the subsequences of the given sequence, we can use a two-dimensional array to store our results. We can start from the beginning of the sequence and keep adding one element at a time. At every step, we will try all of its subsequences. So for every startIndex and endIndex in the given string, we will choose one of the following two options:
If the element at the startIndex matches the element at the endIndex, the length of LPS would be two plus the length of LPS till startIndex+1 and endIndex-1.
If the element at the startIndex does not match the element at the endIndex, we will take the maximum LPS created by either skipping element at the startIndex or the endIndex.
So our recursive formula would be:
if st[endIndex] == st[startIndex]
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = 2 + dp[startIndex + 1][endIndex - 1]
else
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = Math.max(dp[startIndex + 1][endIndex], dp[startIndex][endIndex - 1])Let’ s draw this visually for “cddpd”, starting with a subsequence of length 1. As we know, every sequence with one element is a palindrome of length 1:
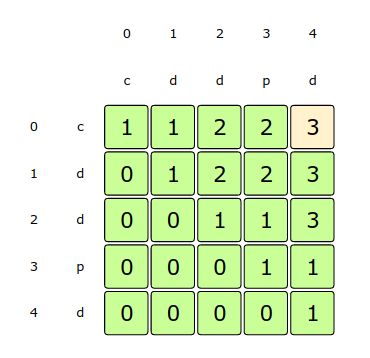
From the above visualization, we can clearly see that the length of LPS is 3 as shown by dp[0][4].
def find_LPS_length(st):
n = len(st)
# dp[i][j] stores the length of LPS from index 'i' to index 'j'
dp = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
# every sequence with one element is a palindrome of length 1
for i in range(n):
dp[i][i] = 1
for startIndex in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
for endIndex in range(startIndex + 1, n):
# case 1: elements at the beginning and the end are the same
if st[startIndex] == st[endIndex]:
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = 2 + dp[startIndex + 1][endIndex - 1]
else: # case 2: skip one element either from the beginning or the end
dp[startIndex][endIndex] = max(
dp[startIndex + 1][endIndex], dp[startIndex][endIndex - 1])
return dp[0][n - 1]
def main():
print(find_LPS_length("abdbca"))
print(find_LPS_length("cddpd"))
print(find_LPS_length("pqr"))
main()✓→ Longest Palindromic Substring